At the core of i-STENTORE’s demonstration activities are five pilots across five European countries, each showcasing innovative combinations of energy storage technologies as key enablers in the transition toward a more sustainable and resilient power grid. This post focuses on Demo 3, Virtual Energy Storage System for Renewable Energy Integration, which is being implemented in Spain, in the province of Granada.
The demo brings together a diverse group of Spanish partners from academia, industry, and technology, creating a highly effective collaborative environment that supports the successful deployment of the proposed use cases. The University Carlos III of Madrid (UC3M) leads the demo and is responsible for developing and implementing the real-time control system for the storage assets. Cuerva is the Distribution System Operator (DSO) of the local grid. CEN Solutions supplies and integrates the Li-ion battery system, while Aggregering (AGG), an ICT service provider, is developing the demo’s cloud-based digital platform. Finally, the University of Málaga (UMA) is in charge of designing the optimization algorithms that will govern the demo’s operation.
Granada: An Ideal Setting for Renewable Energy Storage Integration
The province of Granada is located in the southeast of Spain, within the region of Andalusia. Its distribution grid is managed by several DSOs, including Cuerva, the DSO representative in the Spanish demo. Cuerva’s network includes over 900 km of distribution lines, more than 500 secondary substations, and two main substations—one of which is connected to the national transmission system (Red Eléctrica). The network serves more than 18,000 supply points, providing electricity to over 50,000 users and delivering an average of 247,000 kWh per day.
Granada offers an ideal context for demonstrating energy storage solutions aimed at facilitating the integration of renewable energy. In 2024 alone, the province added 186 MW of new renewable capacity, and 118 additional renewable energy projects—representing a combined 1,664 MW—are currently under review.
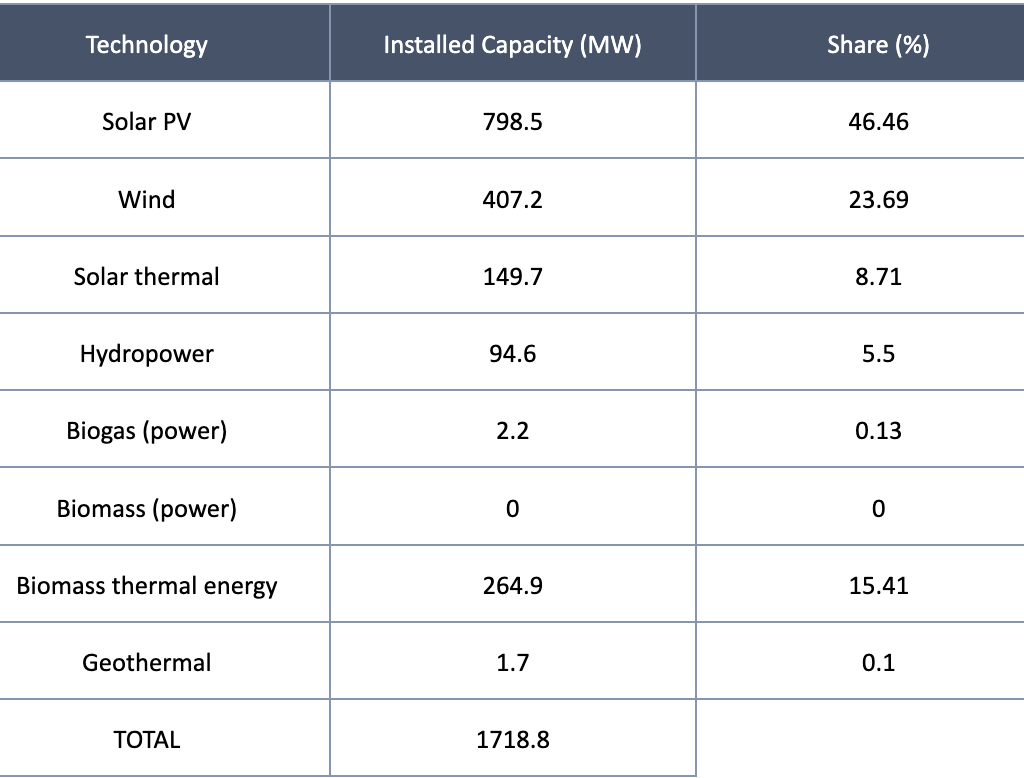
According to the Andalusian Energy Agency, Granada stands out for its high levels of renewable energy production. By the end of 2024, its installed renewable capacity had reached 1,718.8 MW. Of this, photovoltaic solar energy accounts for 46.46%, while wind power represents 23.69%, with the remaining share distributed among other renewable technologies. The breakdown of installed capacity by technology is detailed in the table below:
The continuously increasing injection of renewable energy into the power system presents a major challenge for grid operators, who must integrate new capacity while maintaining stable voltage and frequency levels. Moreover, the weather-dependent and variable nature of renewable generation complicates the controllability of different generation units, as well as the operation and planning of the distribution grid.
Energy storage systems have emerged as a crucial solution to address these challenges, thanks to the advanced control capabilities they provide.
In this context, the province of Granada offers an ideal environment for Demo 3, which integrates two complementary battery energy storage solutions — Lithium-ion and Vanadium Redox Flow technologies — into the distribution grid operated by Cuerva. These storage assets will be managed through a Hierarchical Operation and Control System (HOCS) and connected to a digital platform that delivers Virtual Energy Storage System (VESS) functionalities.
Key Objectives and Operation of Demo 3
Demo 3 aims to demonstrate the coordinated and joint operation of these two energy storage systems, actively participating in energy markets and providing a variety of services to both the DSO and the Transmission System Operator (TSO). The combined operation of these assets is designed to consider the forecasted generation from the associated renewable plants, integrating this data into optimization algorithms that generate optimal participation profiles.
The renewable power plants involved in this demo include a 2 MW photovoltaic (PV) plant, a 2.4 MW wind farm, and a 3 MW run-of-the-river hydroelectric plant.
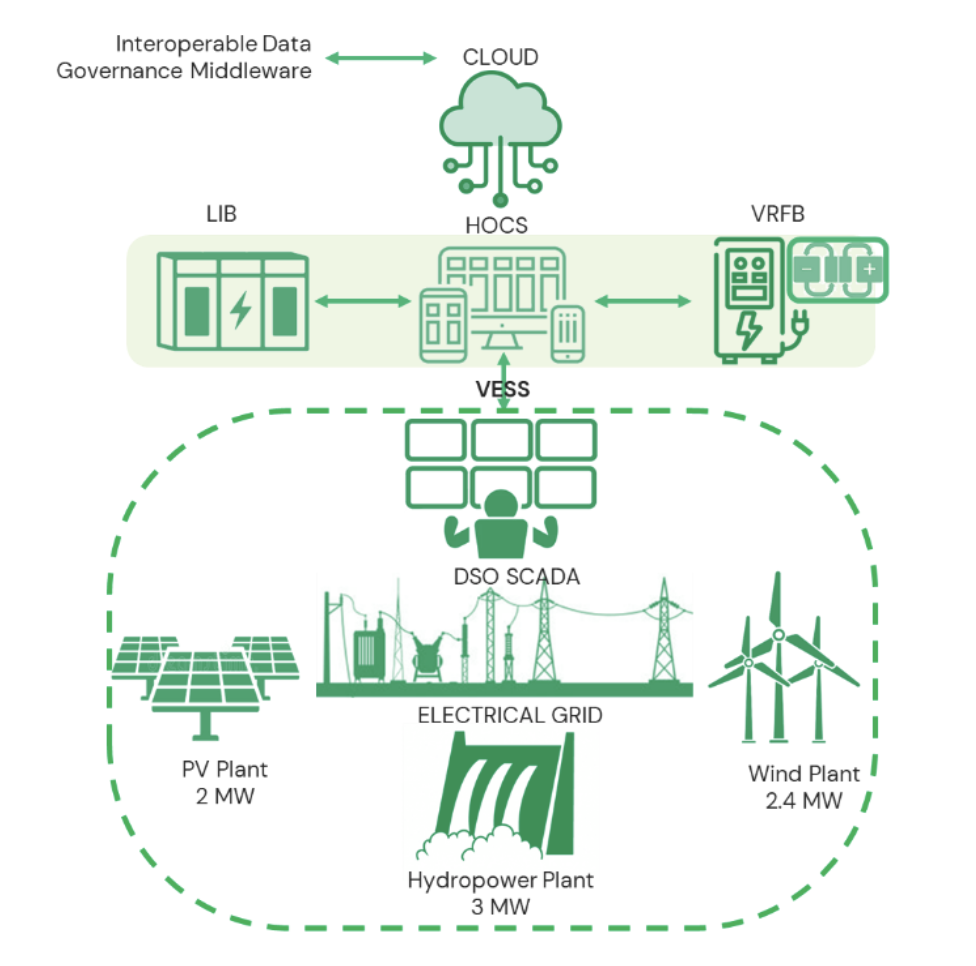
Another fundamental element of Demo 3 is its multi-layer control architecture. The upper layer is managed by the demo’s digital platform, which is cloud-based and hosts the optimization engine. This platform facilitates communication between the various components of the demo as well as with the broader i-STENTORE digital ecosystem.
The intermediate layer consists of a central controller responsible for the real-time execution of the demo. It adjusts the output of the storage assets based on actual grid conditions, monitored at the Point of Connection (POC). At the lowest layer, local controllers embedded within the storage systems handle direct control actions.
This architecture has been specifically designed to enable the demonstration of key use cases, including:
- Participation in the Day-Ahead Market (DAM) for energy arbitrage,
- Participation in the Tertiary Reserve Market to support the TSO’s frequency regulation system, and
- Provision of flexibility services to the DSO.
In this context, Demo 3 aims to achieve several core objectives: optimizing storage services by leveraging the complementary characteristics of the technologies integrated into the Virtual Energy Storage System; enhancing the business case for both the energy storage systems and the associated renewable plants; and promoting higher penetration of renewable energy within the grid area supported by the VESS.
Additionally, the demo contributes to improved grid performance through the dynamic and coordinated response of the storage units. It also demonstrates how multiple stakeholders—such as the VESS operator, renewable plant operators, and DSOs—can interact in an open, secure, and efficient manner via the VESS digital platform. Finally, the demo explores how this digital management platform can interface with other data spaces to further improve overall system performance.
In conclusion, Demo 3 represents a significant step forward in demonstrating how advanced energy storage systems, supported by intelligent control and digitalisation, can accelerate the integration of renewable energy into the grid. By showcasing a real-life application in a complex and renewable-rich environment like Granada, this demo not only validates technical solutions but also opens the door to future business models and cooperation frameworks that are essential for a more resilient, flexible, and sustainable energy system.
Author(s): Carolina María Martín Santos (UNIVERSIDAD CARLOS III DE MADRID)
Share now!

